This article takes a deep dive into the European SEO expert: how much is the typical SEO budget? How much is spent on tools? What type of SEO work is done? What are the types of employment? This article is part of the international report SEO & Content Marketing 2023 by WhitePress and is used with explicit permission. Download the full report with expert comments for NL here.
How much do European specialists spend on SEO?
Widely available information about their website optimization spending does not make it any clearer. Search Engine Journal reports an average of less than USD 500 per month; according to WebFx, it is between USD 750 and 2,000; in research by Ahrefs, the budget was precisely USD 3209; and Accelerate Agency reports that it should be expected to spend between USD 1,000 and… USD 1 million. Not only is this range vast, but the data usually comes only from the US market, so it is not entirely representative of Europe.
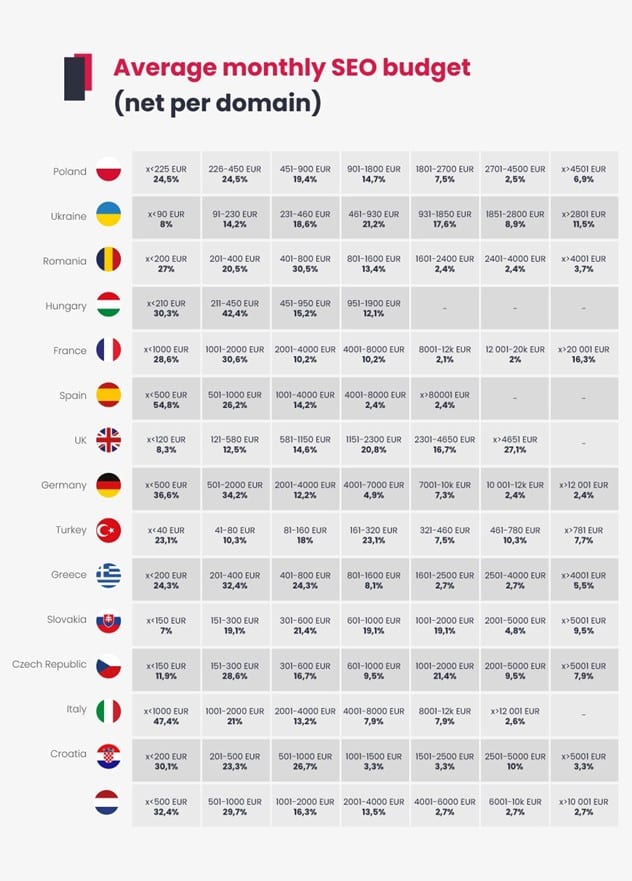
A study by WhitePress® allowed for more concrete results. It seems that, in Europe, the most money is spent by people in countries such as the UK, where 27% of SEO specialists have a monthly budget of more than EUR 4540 for a domain. Czechs, Poles, or Romanians tend to have budgets of EUR 400–500, which probably also has to do with the size of the market. The lowest budgets can be found in Turkey, where only half of SEO specialists invest more than EUR 200 per month in their websites. The results are highly variable, but the average budget per domain oscillates around EUR 500 per month.
What is the cost of tools?
To gain a competitive edge in today’s saturated SEO-marketing market, staying up-to-date with the latest tools is essential. The days of relying solely on free SEO tools like Google Search Console are long gone, although there are exceptions. Many SEO specialists now leverage their own custom tools or unique combinations of techniques. The number of officially available tools exceeds 200, and the possibilities for proprietary tools are endless.
The expenditures of most European SEO specialists are no more than a few hundred Euros per month.
While Google Search Console remains a valuable tool for providing insights into site rankings, it has certain limitations. For instance, it only offers traffic estimates and lacks the ability to compare a site with its competitors, a feature provided by paid tools. Information from these paid equivalents can confer an advantage, as not everyone has access to them. Additionally, they enable verification of elements beyond the scope of Google Search Console.
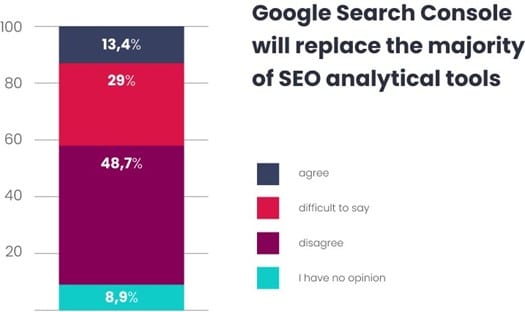
However, is there a chance that Google Search Console will once again become the sole tool used by SEO specialists? The limitations of it are acknowledged by our respondents, with only 13% of them expressing readiness to state that it will replace most analytics tools in the future.
The limitations of this tool are noticeable — it’s difficult to work in current times using just one tool, especially in such a complicated field like SEO.
Types of SEO work done in Europe
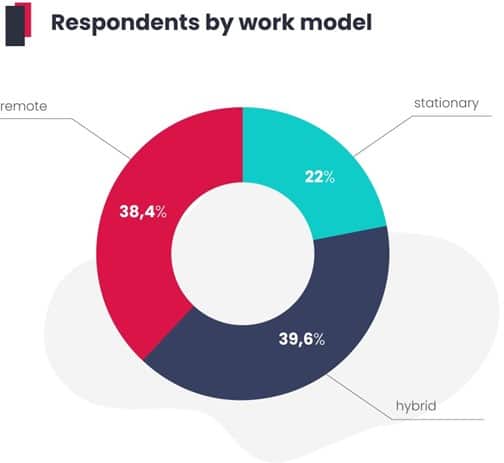
Do we know anything more about the specifics of the European market? The last few years have witnessed a veritable revolution in the field of remote working, and the SEO industry reflects this. Only one in five SEO specialists works in a corporate office. The rest perform their duties in hybrid or remote mode. How does the widespread use of remote work in recent years impact work?
Types of employment and new SEO challenges
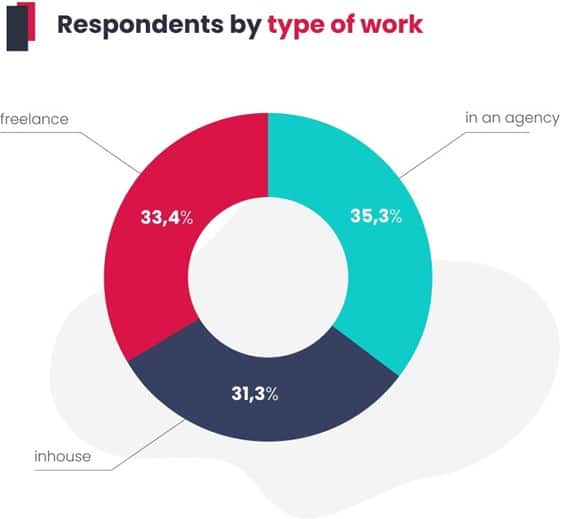
When it comes to how SEO specialists are employed, there are roughly equal numbers of those working in agencies, freelancers, and people employed directly by a company that positions its own sites.
The majority (65%) are involved not only in sole SEO but also in other areas such as social media advertising, SEM, or email marketing.
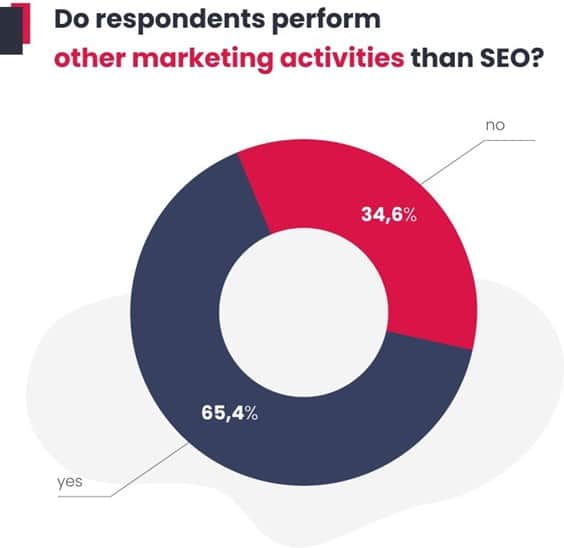
There are various reasons for this. Freelancers demonstrate versatility to gain a market advantage. A company’s in-house specialists are often responsible for other areas out of necessity, as they handle all or a large part of the company’s online marketing themselves. Whereas, in an agency, it is sometimes necessary to combine several roles to achieve better results for the ordering parties on tight budgets.
This reflects a common market trend to combine SEO with other activities as part of holistic marketing strategies.
It is confirmed by the results of previous reports concerning other industries: 69% of marketers use SEO alongside marketing techniques (HubSpot State of Marketing Report, 2021), and the phrase “SEO in content marketing” was the second most searched for content-related topics last year (The State of Content Marketing, 2022 Global Report), which means that marketers or copywriters are also keen to add SEO to their arsenal.
As can be seen, these areas are more often perceived by both parties as complementary than competitive.
The question of the number of handled domains is also indirectly linked to the type of employment. Only one domain is usually handled by SEO specialists employed by a specific company, while handling more than 15 sites is definitely more popular among agencies and freelancers.
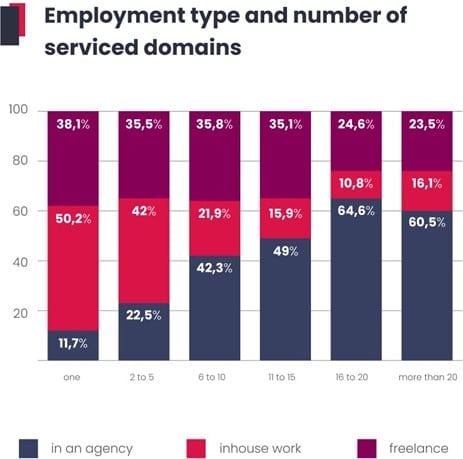
From a global perspective, the largest number of people (more than 37%) work on 2–5 domains at a time; these can be agency employees with several major clients, the aforementioned freelancers, as well as in-house staff. In the WhitePress® study, almost 70% of respondents do not work on more than 10 websites.
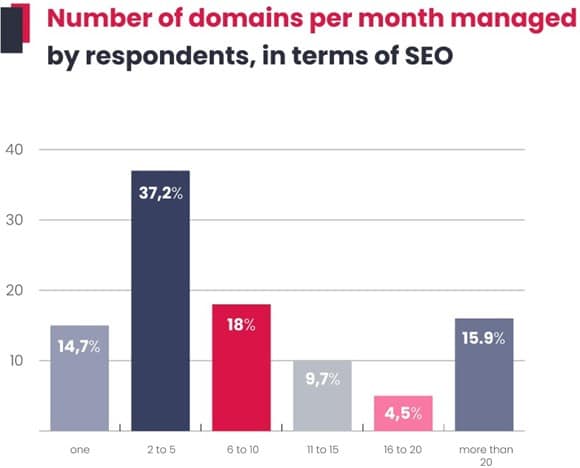
Therefore, finding balance is crucial. The specialist needs to have a sufficient number of websites to stay engaged and up-to-date with the industry, but not so many that their work becomes superficial and lacking in in-depth understanding.
Ultimately, there is no fixed number that guarantees effectiveness for every SEO specialist. It depends on their capabilities, time management skills, and ability to stay informed about the latest SEO trends and best practices.
Striking the right balance ensures that the specialist can deliver quality results across the supervised websites.
SEO industry and gender
And who is an SEO specialist today? Slowly but steadily, the representation of women in the industry is growing, changing an image that so far has been heavily masculine.
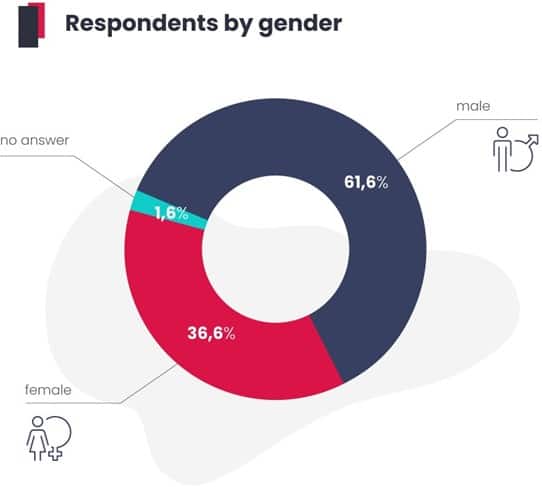
A Moz report from 2015 and a paper entitled State of SEO from 2020 show that at that time, approximately 30% of SEO specialists were female in 2015. Meanwhile, in our 2022–2023 research, the result has already risen to more than 36 percent. Incidentally, we found that, proportionally, the largest number of women in SEO works in Greece.
In terms of the digital world, worldwide data largely reflects that of the survey for gender. Similarweb reviewed three popular SEO websites: Search Engine Journal, Search Engine Land, and SEOroundtable to see the gender split of website visitors. As you can see below, the data sits around the 60% male vs. 40% female mark worldwide.
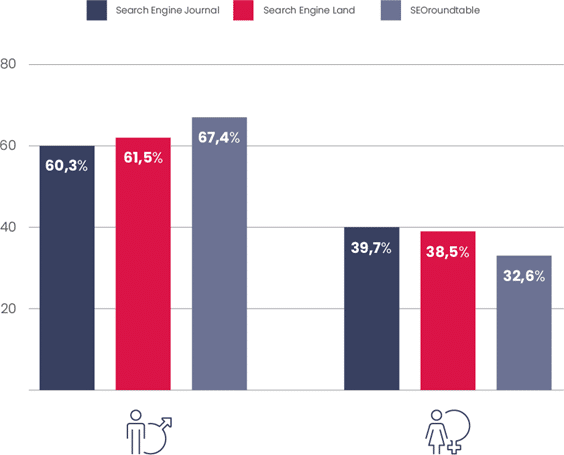
In a number of European countries, this gender split is nearing an even split. For instance, in the UK, 40% of visitors to SEJ are female, and in Poland, it’s 48%. This extends to industry events, where we’ve seen a transformation in the demographic. In fact, when you look at the traffic going to the BrightonSEO website, females edge the majority with 52%.
This article is part of the international report SEO & Content Marketing 2023 by WhitePress and is used with explicit permission. Download the full report for NL with expert comments here.